Agung Volcano
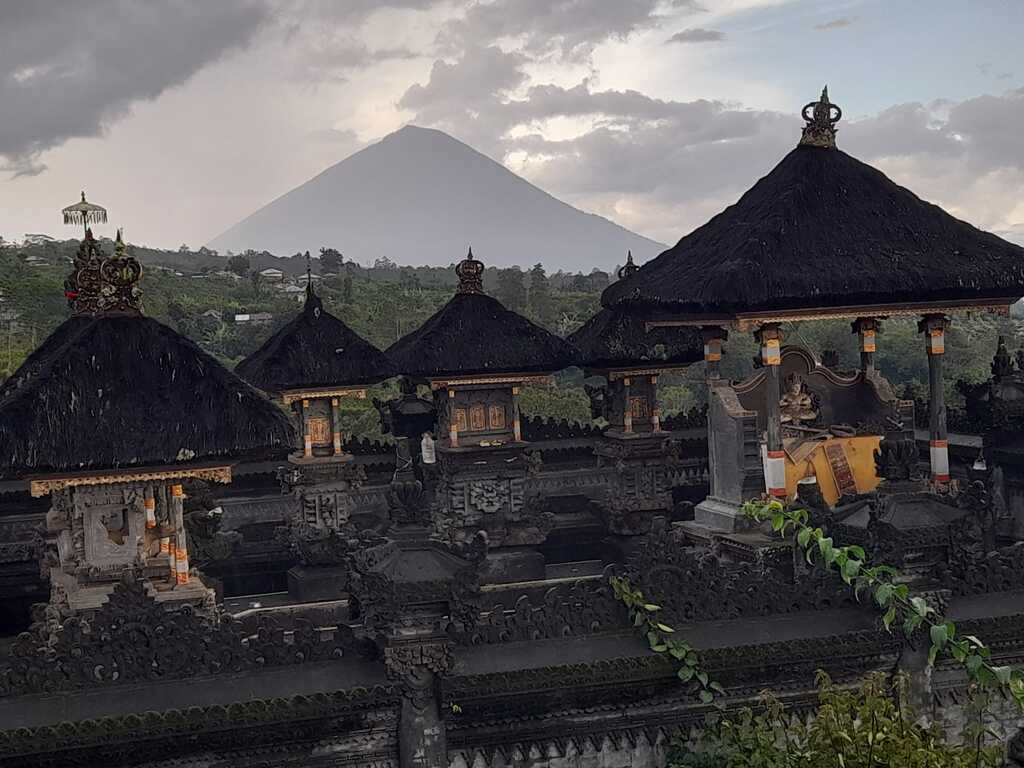

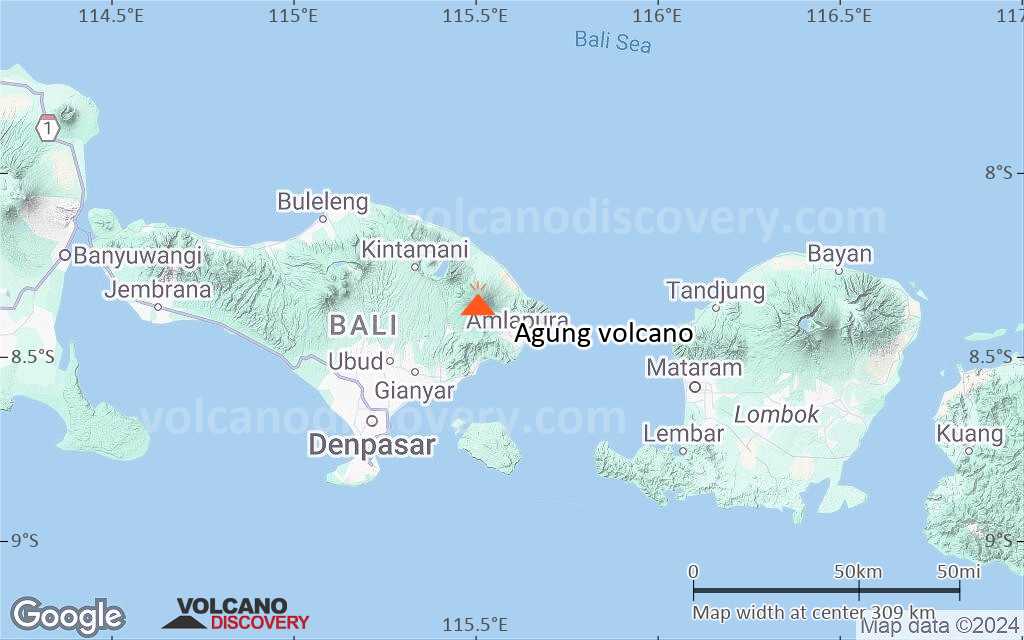
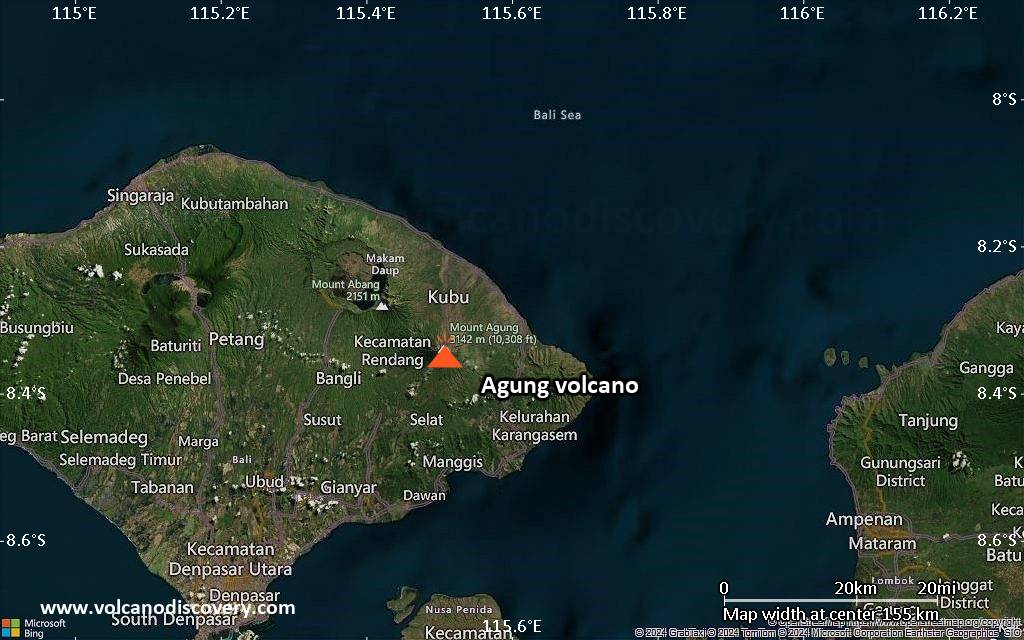
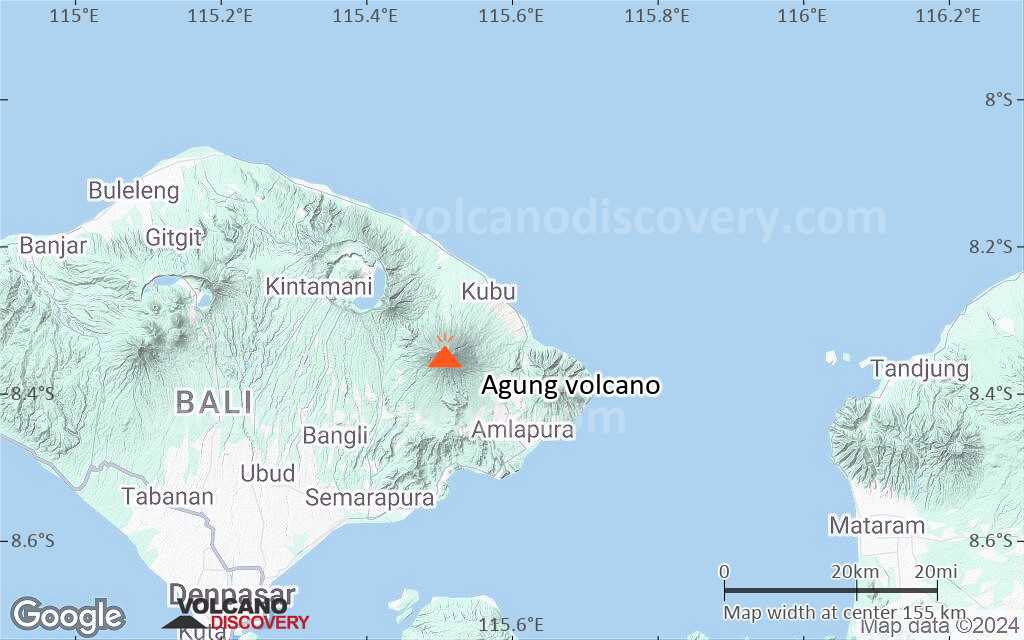
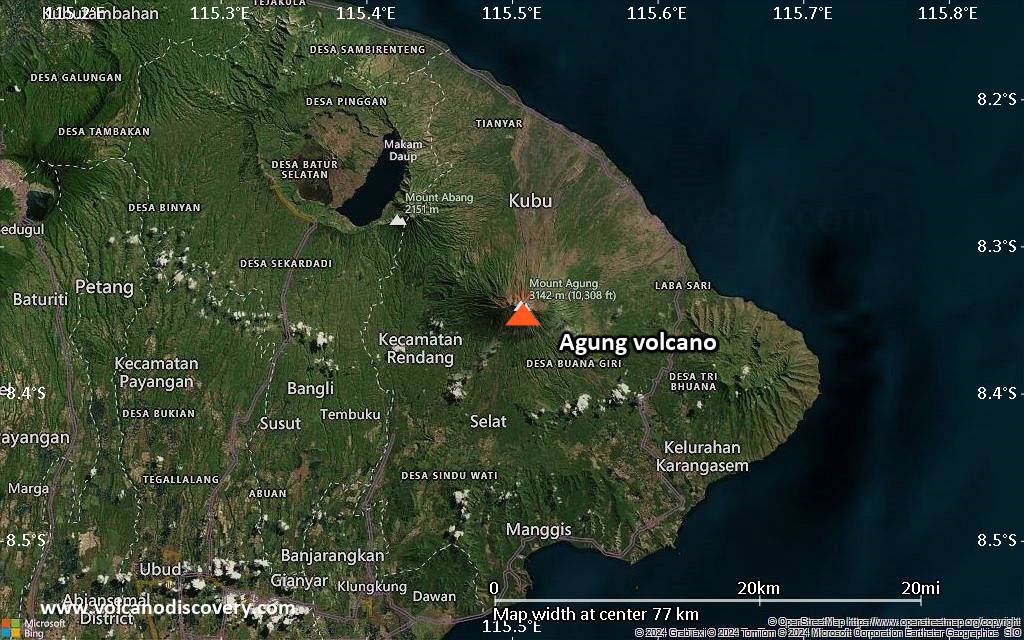
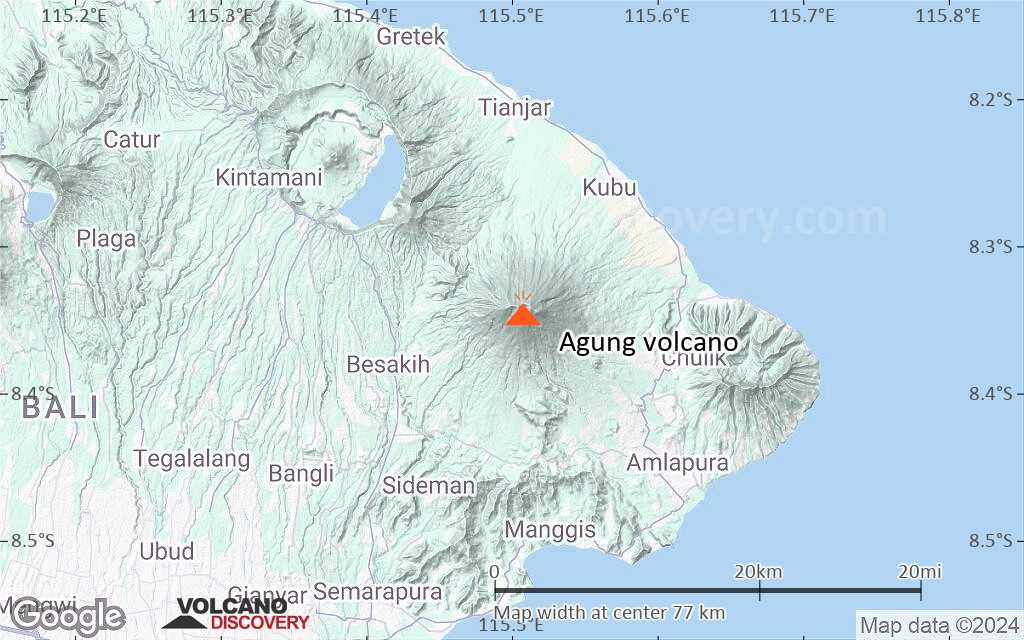
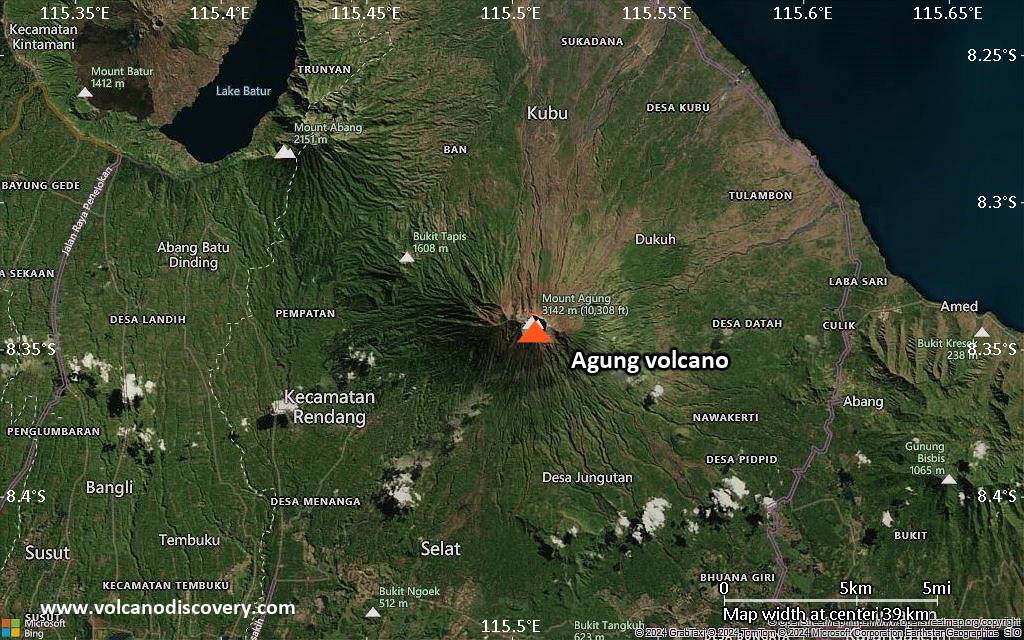
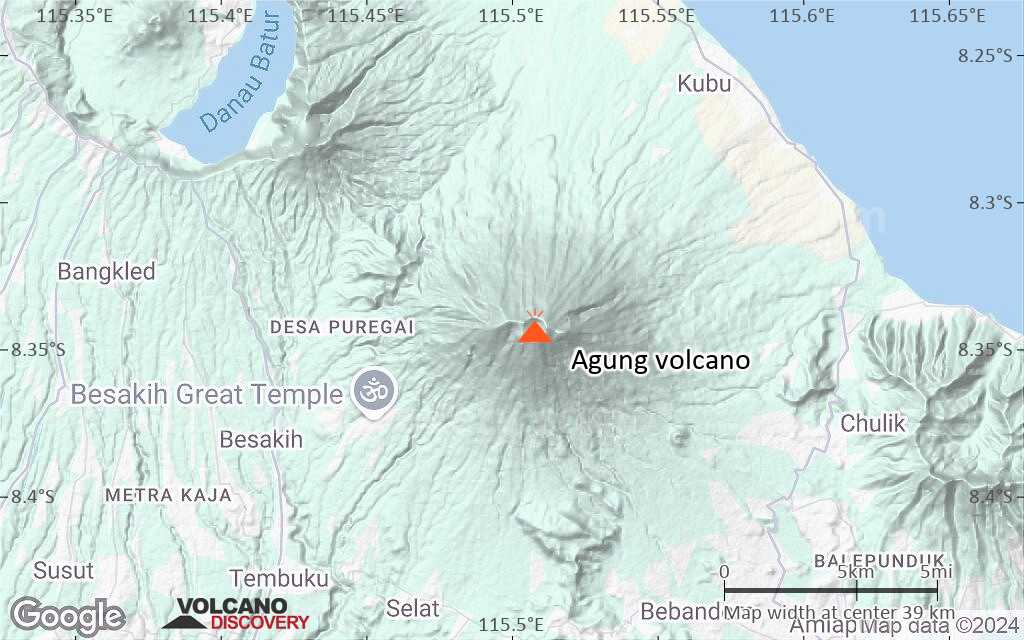
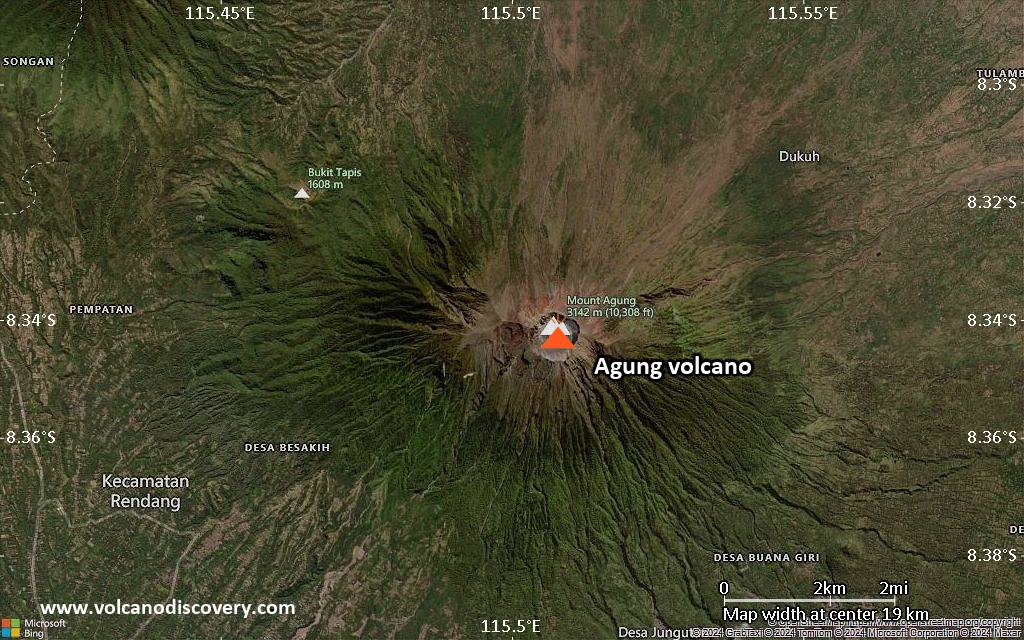
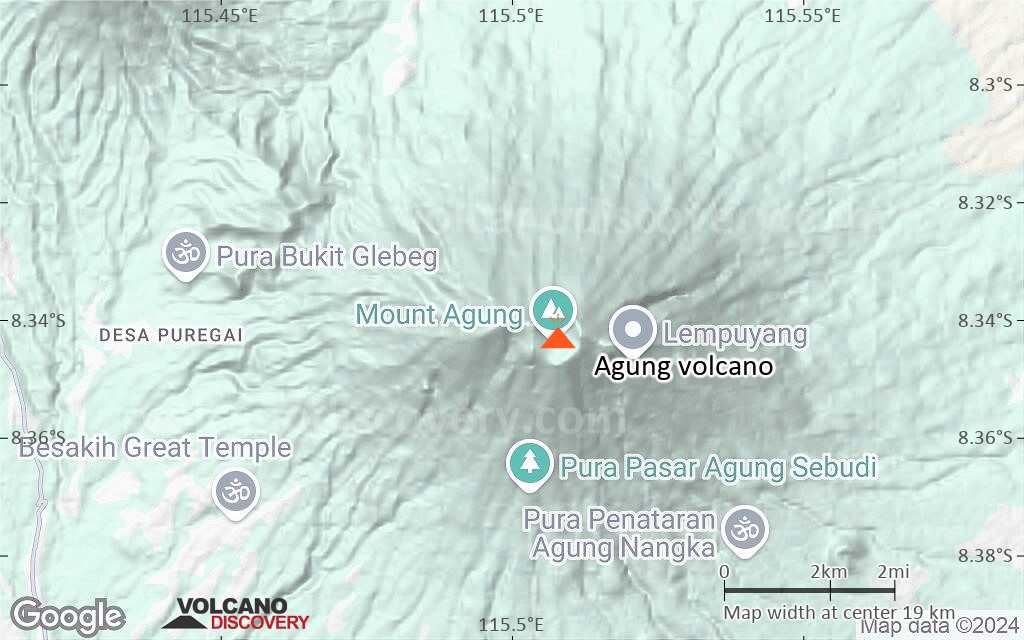
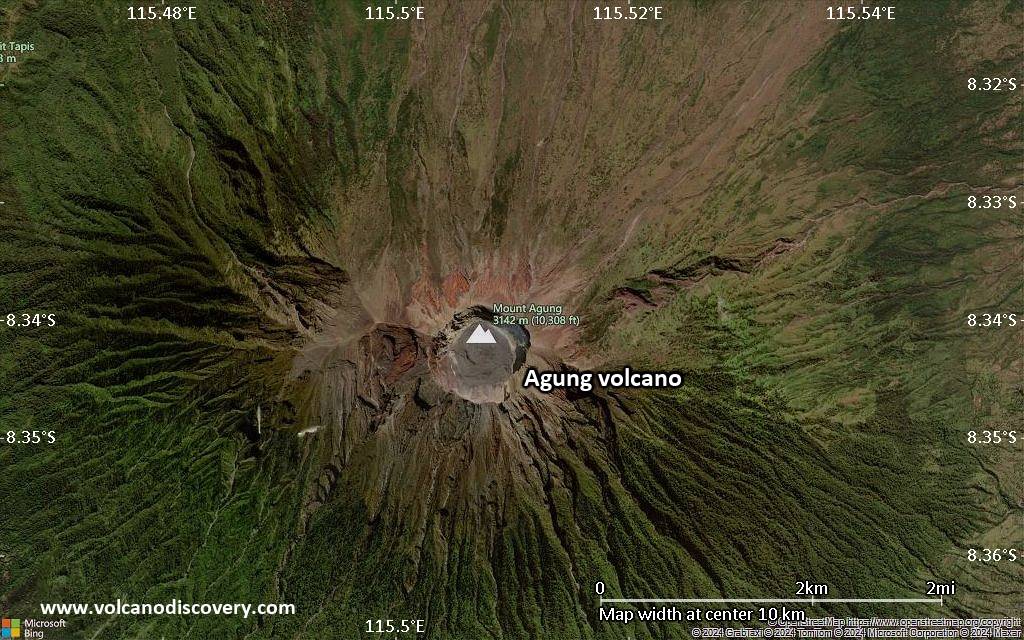
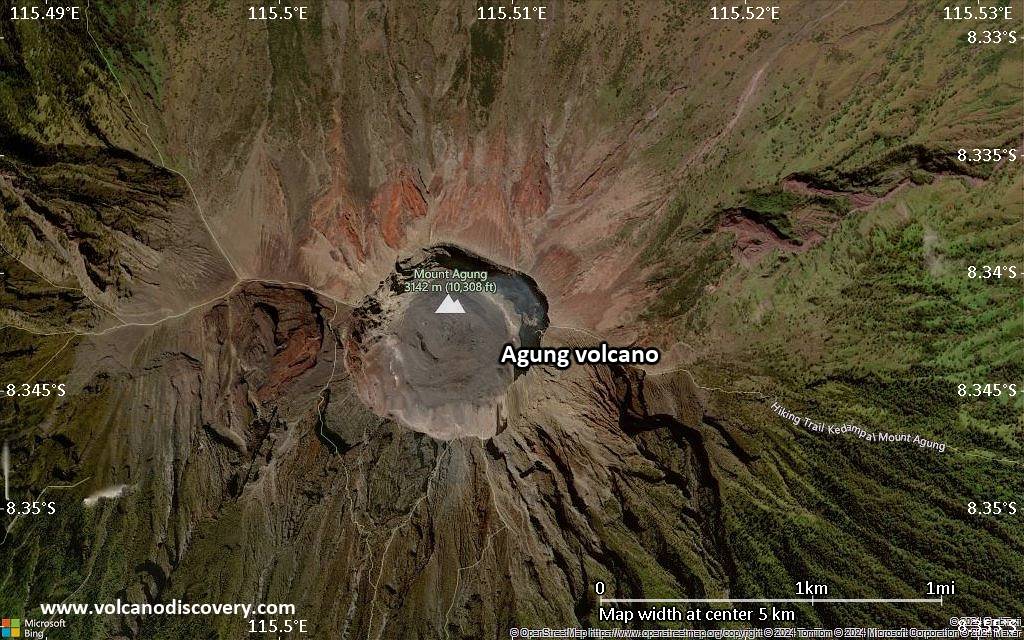
Mount Agung or Gunung Agung is a active volcano in Bali. This stratovolcano is the highest point on the island. It dominates the surrounding area influencing the climate. The clouds come from the west and Agung takes their water so that the west is lush and green and the east dry and barren.
Agung volcano eruptions: 1808, 1821(?), 1843, 1963-64 (large Plinian eruption on March 16, 1963), 2017-ongoing
Latest nearby earthquakes
| Date and Time | Mag / Depth | Distance / Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Background
Mount Agung or Gunung Agung is a mountain in Bali. This stratovolcano is the highest point on the island. It dominates the surrounding area influencing the climate. The clouds come from the west and Agung takes their water so that the west is lush and green and the east dry and barren.Gunung Agung last erupted in 1963-64 and is still active, with a large and very deep crater which occasionally belches smoke and ash. From a distance, the mountain appears to be perfectly conical, despite the existence of the large crater.
From the peak of the mountain, it is possible to see the peak of Mount Rinjani on the island of Lombok, although both mountains are frequently covered in cloud.
The 1963 eruption of Agung volcano
After more than 100 years of slumber, Mt. Agung came back to life on February 18, 1963. Loud noises and a cloud rising from the crater were noticed, then the ejection of bombs and blocks.
On February 24, 1963, highly viscous lava flows began to travel down the northern flank of the volcano, reaching a length of 7 km in about 18 to 20 days and an elevation of 510 m above sea level. The flows were about 0.5-0.8 km wide and 30-40 m thick. Rough estimates indicate a total volume of these flows of about 50 million cubic meters.
After that phase, the eruption became more and more explosive, and on March 17, 1963, the paroxysmal sub-Plinian eruption took place, generating a eruptino column of 8-10 km height that collapsed to form devastating pyroclastic flows. These flows reached distances of up to 15 km from the crater following vallezs to the south and east, at speeds of about 60 km/hour. Many villages were destroyed and more than 1000 people lost their lives. Heavy tephra fall occurred in areas west of the volcano, where up to 50-70 cm of ash were deposited.
In May, the south peak of the crater wall collapsed, lowering its height for about 200 meters. The lowest crater wall at present is the upper end of Langon river (2600 m).
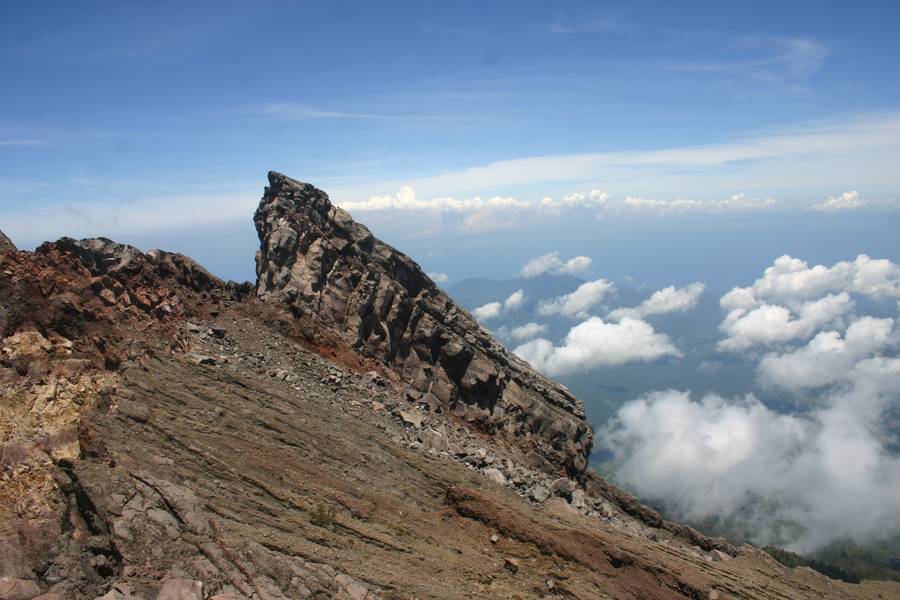
Agung Volcano Photos




Significant volcanic eruptions: Agung volcano
| Date | Note | VEI | Deaths | Damage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summit crater Historical obs./docs. | 3 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 5 | ||||
| 1963 May 16 (eruption | Historical obs./docs. | 3 | 120 | Info | |
| 1963 Mar 18 (eruption | Tsunami recorded Historical obs./docs. | 5 | 1,028 | Info | |
Historical obs./docs. | 5 | ||||
?? | Uncertain Eruption | 2 | |||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Agung Volcano FAQ
+When was the last eruption of Agung volcano?
The last confirmed eruption of Agung occurred during 2017 - 2019.
+How often does Agung volcano erupt?
Since 1808, Agung volcano has had at least 4 historically documented eruptions. This means that it erupts on average every 54 years.
Many eruptions of Agung have lasted more than one year. In total, the volcano has been in eruption during 7 out of 217 years until now. In other words, Agung has been active at least one in 31 years on average. Note that this value is likely an underestimate, because the known history of eruptions from Agung is likely incomplete, especially further back in time.
+How active is Agung volcano at present?
Agung volcano is occasionally active: Since 1900, it has had 5 eruptions, and been active during 5 years out of 126 as of now. This means, Agung has been in eruption one in 25.2 years on average. The last eruption was from 2017 until 2019 and ended 6 years ago.
+When was the largest eruption of Agung volcano?
The largest eruption of Agung volcano in historic times occurred during 1963 - 1964. It ranks as a plinian eruption with a magnitude 5 on the VEI (Volcanic Explosivity Index) scale. Eruption of this size are often catastrophic on a regional scale.
Latest satellite images
Agung Volcano Maps